Profile

|
Publications
A Physically Consistent Implicit Viscosity Solver for SPH Fluids
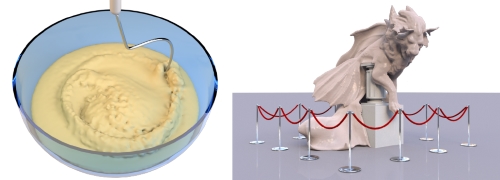
In this paper, we present a novel physically consistent implicit solver for the simulation of highly viscous fluids using the Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) formalism. Our method is the result of a theoretical and practical in-depth analysis of the most recent implicit SPH solvers for viscous materials. Based on our findings, we developed a list of requirements that are vital to produce a realistic motion of a viscous fluid. These essential requirements include momentum conservation, a physically meaningful behavior under temporal and spatial refinement, the absence of ghost forces induced by spurious viscosities and the ability to reproduce complex physical effects that can be observed in nature. On the basis of several theoretical analyses, quantitative academic comparisons and complex visual experiments we show that none of the recent approaches is able to satisfy all requirements. In contrast, our proposed method meets all demands and therefore produces realistic animations in highly complex scenarios. We demonstrate that our solver outperforms former approaches in terms of physical accuracy and memory consumption while it is comparable in terms of computational performance. In addition to the implicit viscosity solver, we present a method to simulate melting objects. Therefore, we generalize the viscosity model to a spatially varying viscosity field and provide an SPH discretization of the heat equation.
» Show BibTeX
@article{WKBB2018,
author = {Marcel Weiler and Dan Koschier and Magnus Brand and Jan Bender},
title = {A Physically Consistent Implicit Viscosity Solver for SPH Fluids},
year = {2018},
journal = {Computer Graphics Forum (Eurographics)},
volume = {37},
number = {2}
}
An hp-Adaptive Discretization Algorithm for Signed Distance Field Generation
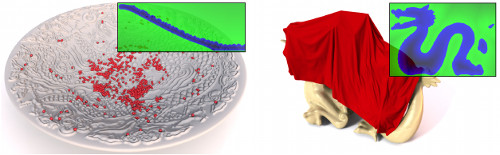
In this paper we present an hp-adaptive algorithm to generate discrete higher-order polynomial Signed Distance Fields (SDFs) on axis-aligned hexahedral grids from manifold polygonal input meshes. Using an orthonormal polynomial basis, we efficiently fit the polynomials to the underlying signed distance function on each cell. The proposed error-driven construction algorithm is globally adaptive and iteratively refines the SDFs using either spatial subdivision (h-refinement) following an octree scheme or by cell-wise adaption of the polynomial approximation's degree (p-refinement). We further introduce a novel decision criterion based on an error-estimator in order to decide whether to apply p- or h-refinement. We demonstrate that our method is able to construct more accurate SDFs at significantly lower memory consumption compared to previous approaches. While the cell-wise polynomial approximation will result in highly accurate SDFs, it can not be guaranteed that the piecewise approximation is continuous over cell interfaces. Therefore, we propose an optimization-based post-processing step in order to weakly enforce continuity. Finally, we apply our generated SDFs as collision detector to the physically-based simulation of geometrically highly complex solid objects in order to demonstrate the practical relevance and applicability of our method.
» Show BibTeX
@Article{KDBB17,
author = {Koschier, Dan and Deul, Crispin and Brand, Magnus and Bender, Jan},
title = {An hp-Adaptive Discretization Algorithm for Signed Distance Field Generation},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics},
year = {2017},
volume = {23},
number = {10},
pages = {1--14},
issn = {1077-2626},
doi = {10.1109/TVCG.2017.2730202}
}

